Transmitting Other Data Types
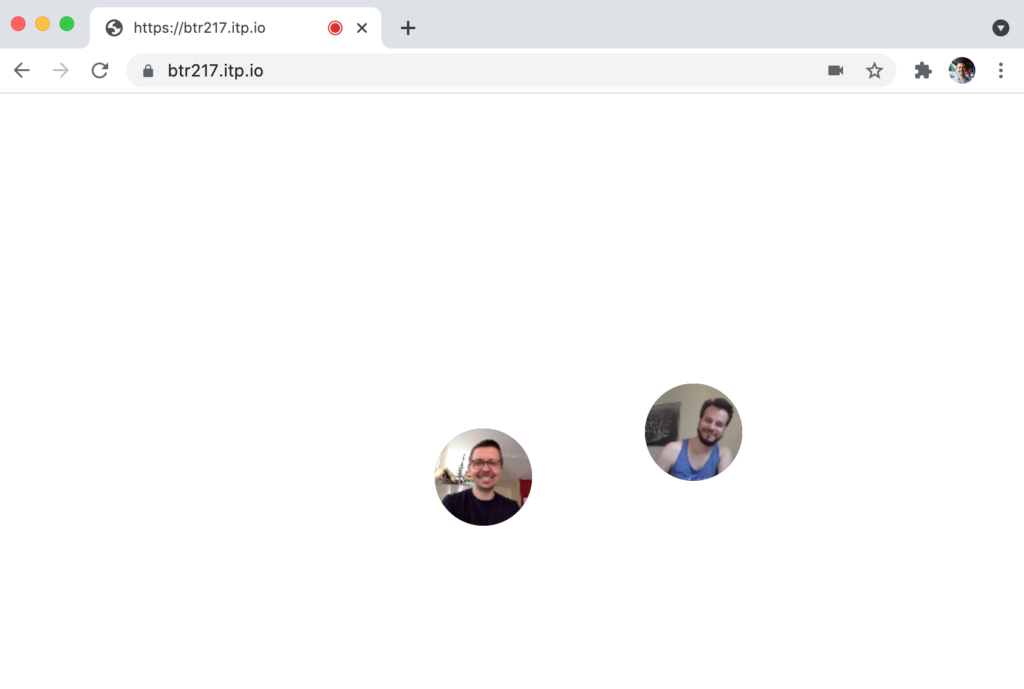
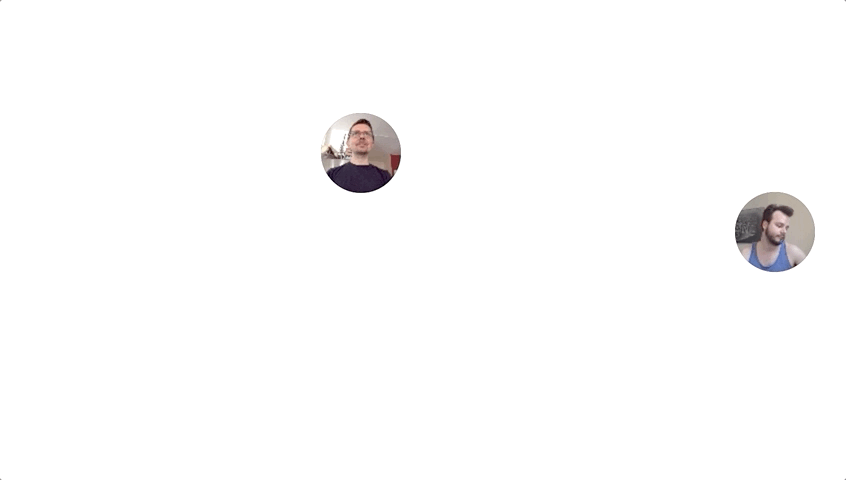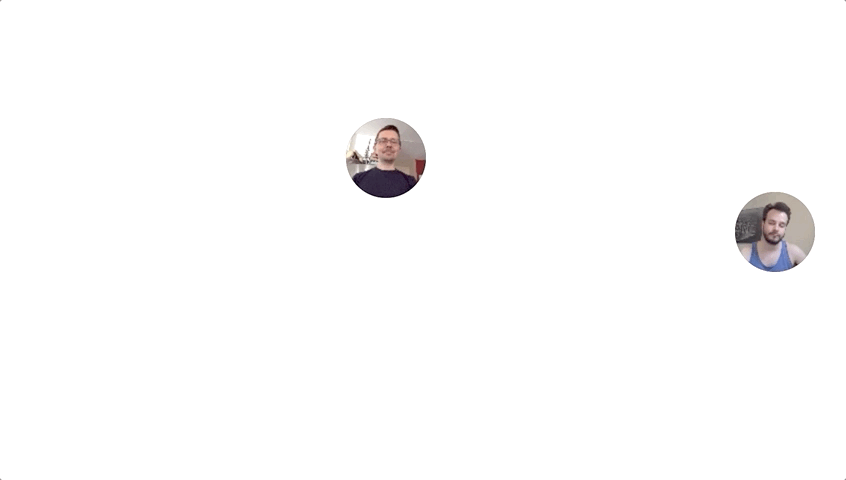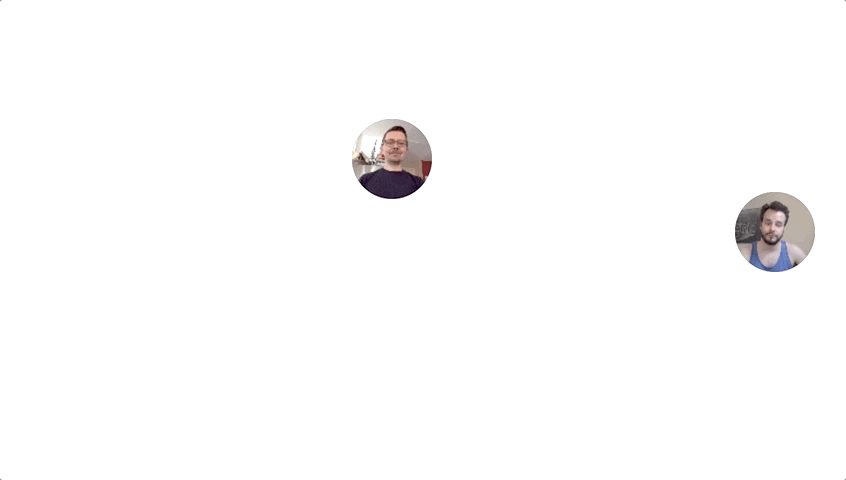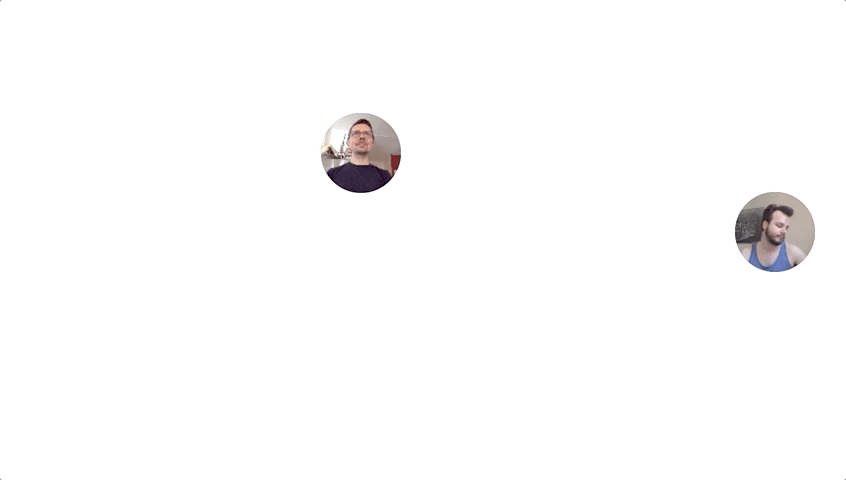
Using getUserMedia and HTTPS Lauren Chong and I were able to make a simple video streaming site that ties a user’s mouse movement to their video camera feed.
To make the video stream more manageable the video resolution and frame rate are reduced in the user’s browser before being sent to the sever.
In the current iteration the resolution is reduced to 1/6 resolution (106 x 80px) and 8 frames per second.
// Variables to control video size and framerate
let videoSize = 6;
let videoFramerate = 8;
// Draw Loop
function draw() {
context.clearRect(0,0,thecanvas.width,thecanvas.height);
context.drawImage(video,0,0,video.width/videoSize,video.height/videoSize);
//console.log(thecanvas.toDataURL());
var dataToSend = {image: thecanvas.toDataURL(), id: socket.id};
socket.emit('image',dataToSend);
}
setInterval(function() { draw(); }, 1000/videoFramerate);
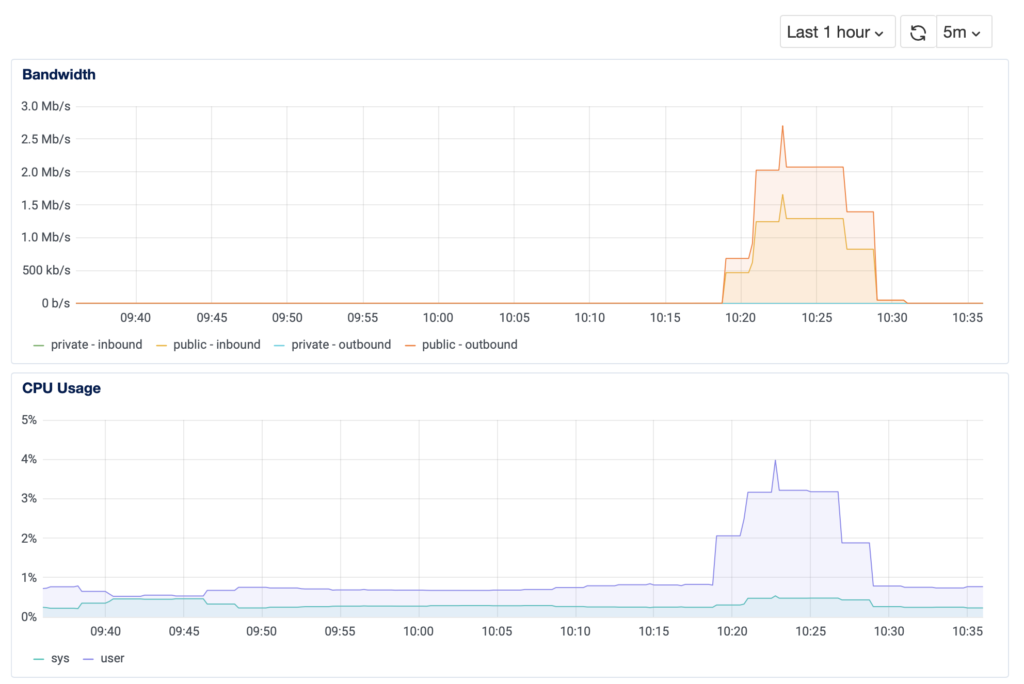
Based on the graph data from Digital Ocean it appears that even with reduced resolution and frame rate the streams consume a considerable amount of bandwidth and CPU usage on the server.
Video lag is an issue with this setup. From a bit of online digging it seems that this is likely due to the use of TCP over UDP with Socket.io. TCP will only send data in order and repeatedly try to send until it goes through, preventing dropped frames but causing lag. UDP on the other hand would allow for dropped frames and a smoother appearance for the end user.
The full index.html file here:
<html>
<head>
<script type="text/javascript" src="/socket.io/socket.io.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">
var socket = io.connect();
var toggleMovement = true;
socket.on('connect', function() {
console.log("Connected");
});
// Receive from image event
socket.on('image', function(imagedata) {
if(document.getElementById(imagedata.id) != null){
document.getElementById('theimage' + imagedata.id).src = imagedata.image;
console.log('moving image');
//var div = document.getElementById(imagedata.id);
}
});
window.addEventListener('load', function() {
// The video element on the page to display the webcam
let video = document.getElementById('thevideo');
// Constraints - what do we want?
let constraints = { audio: false, video: true }
// Prompt the user for permission, get the stream
navigator.mediaDevices.getUserMedia(constraints).then(function(stream) {
/* Use the stream */
// Attach to our video object
video.srcObject = stream;
// Wait for the stream to load enough to play
video.onloadedmetadata = function(e) {
video.play();
draw();
};
})
.catch(function(err) {
/* Handle the error */
alert(err);
});
// Hide Cursor
document.body.style.cursor = 'none';
var thecanvas = document.getElementById('mycanvas');
var context = thecanvas.getContext('2d');
context.fillStyle="#0000FF";
thecanvas.addEventListener('mousemove', function(evt) {
context.fillRect(evt.clientX,evt.clientY,20,20);
})
// Variables to control video size and framerate
let videoSize = 6;
let videoFramerate = 8;
// Draw Loop
function draw() {
context.clearRect(0,0,thecanvas.width,thecanvas.height);
context.drawImage(video,0,0,video.width/videoSize,video.height/videoSize);
//console.log(thecanvas.toDataURL());
var dataToSend = {image: thecanvas.toDataURL(), id: socket.id};
socket.emit('image',dataToSend);
//requestAnimationFrame(function() { draw(); });
}
setInterval(function() { draw(); }, 1000/videoFramerate);
// Possibly a better alternative -->
//requestAnimationFrame(function() { draw(); });
// Share mouse position
document.body.addEventListener('mousemove', function(evt) {
//console.log(evt);
if(toggleMovement){
var dataToSend = {x: evt.clientX, y: evt.clientY, id: socket.id};
socket.emit('mouse', dataToSend);
}
});
// Toggle Movement
document.body.addEventListener('click', function(evt) {
//console.log(evt);
toggleMovement = !toggleMovement;
// Hide Cursor
if(toggleMovement){
document.body.style.cursor = 'none';
} else {
document.body.style.cursor = 'pointer';
}
});
});
// When receiving a mouse position tie to video div
socket.on('mouse', function (data) {
//console.log(data);
let newDiv;
if(document.getElementById(data.id) == null) {
// create a new div element
// console.log(data.id + ' does not exist as a DIV and evaluates as null');
newDiv = document.createElement("div");
newDiv.id = data.id;
newDiv.innerHTML = '<img id="theimage' + data.id + '" width="100" height="100" style="-webkit-transform: scaleX(-1);transform: scaleX(-1);">';
newDiv.style.position = "absolute";
newDiv.style.width = "80px";
newDiv.style.height = "80px";
newDiv.style.borderRadius = "40px";
newDiv.style.overflow = "hidden";
newDiv.style.backgroundColor = "#000000";
} else {
// get existing div
newDiv = document.getElementById(data.id);
}
// set div position
newDiv.style.top = data.y + "px";
newDiv.style.left = data.x + "px";
document.body.appendChild(newDiv);
//console.log(newDiv);
});
// User disconnect
socket.on('deleteUser', function(userID) {
var disconnectedUser = document.getElementById(userID);
disconnectedUser.remove();
console.log('User ' + userID + ' disconnected.');
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<video id="thevideo" width="640" height="480" muted hidden></video>
<canvas width="100" height="100" id="mycanvas" hidden></canvas>
<!-- <img id="theimage" width="100" height="80"> -->
</body>
</html>
And the server.js file:
// We need the file system here
var fs = require('fs');
// Express is a node module for building HTTP servers
var express = require('express');
var app = express();
// Tell Express to look in the "public" folder for any files first
app.use(express.static('public'));
// If the user just goes to the "route" / then run this function
app.get('/', function (req, res) {
res.send('Hello World!')
});
// Here is the actual HTTP server
// In this case, HTTPS (secure) server
var https = require('https');
// Security options - key and certificate
var options = {
key: fs.readFileSync('star_itp_io.key'),
cert: fs.readFileSync('star_itp_io.pem')
};
// We pass in the Express object and the options object
var httpServer = https.createServer(options, app);
// Default HTTPS port
httpServer.listen(443);
// WebSocket Portion
// WebSockets work with the HTTP server
var io = require('socket.io')(httpServer);
var users = [];
// Register a callback function to run when we have an individual connection
// This is run for each individual user that connects
io.sockets.on('connection',
// We are given a websocket object in our function
function (socket) {
console.log("We have a new client: " + socket.id);
users.push(socket);
var usernames = [];
for (var i = 0; i < users.length; i++) {
usernames.push(users[i].username);
}
socket.emit('users',usernames);
socket.on('username', function(data) {
socket.username = data;
var usernames = [];
for (var i = 0; i < users.length; i++) {
usernames.push(users[i].username);
}
io.emit('users',usernames);
});
socket.on('blink', function(data) {
io.emit('blink', data);
});
socket.on('mouse', function(data) {
io.emit('mouse', data);
});
socket.on('image', function(data) {
io.emit('image', data);
});
// When this user emits, client side: socket.emit('otherevent',some data);
socket.on('chatmessage', function(data) {
// Data comes in as whatever was sent, including objects
console.log("Received: 'chatmessage' " + data);
// Send it to all of the clients
//socket.emit()
// Goes to everybody
io.emit('chatmessage', data);
//socket.broadcast.emit('chatmessage', data);
});
socket.on('disconnect', function() {
console.log("Client has disconnected " + socket.id);
io.emit('deleteUser', socket.id);
});
}
);